fibre saturation point
Despite this fact the moisture content in trees can vary widely depending on season species and site. Summary and Conclusions Commercial solar drying of softwood dimension lumber appears uneconomical at this time under the assumed conditions.

Fiber Saturation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
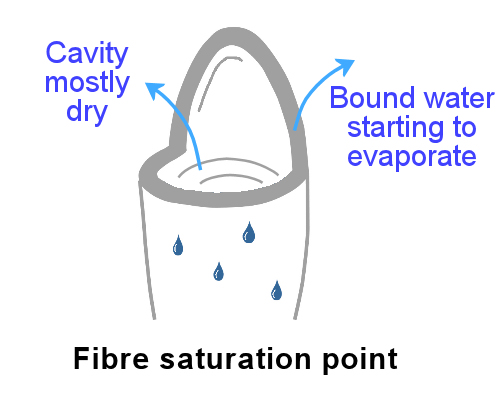
The fibre saturation point FSP is defined as the moisture content at which free water should be completely gone while the cell walls are saturated with bound water.

. But the interior is still wet and has not shrunk. The fiber saturation point MC fs is the point at which all free water has evaporated and the cell walls are completely saturated. The moisture content changes below the fiber saturation point cause lost of bound.
This review is about the behaviour of water in cell walls. As a rule of thumb above 30 moisture content the fiber saturation point in woody tissues free water begins to accumulate. The shrinkage of wood starts at the fiber saturation point nominally 30 moisture content and is nearly linear to complete dryness.
The fiber saturation point FSP is an important parameter of wood material related to dimensional stability and variations of mechanical performance. The moisture content that corresponds to a complete loss of free water with 100 percent of the bound water remaining is known as the fiber saturation point. However in the normal drying of lumber the surface of the wood dries first.
In the living tree the moisture contents of wood are essentially always above the fiber saturation point even in HW. The point in drying wood at which all free moisture has been removed from the cell itself while the cell wall remains saturated with absorbed moisture. When wood reaches its fiber saturation point it can hold no more bound water.
Below the fiber saturation point. Fiber Saturation PointThe stage in the drying or wetting of wood at which the cell walls are saturated and the cell cavities free from water. The fiber saturation point FSP is an important parameter of wood material related to dimensional stability and variations of mechanical performance.
The fiber saturation point often is considered as that moisture content below which the physical and mechanical properties of wood begin to change as a function of moisture content. When the surface dries below the fiber saturation point it begins to shrink. Reduction of moisture content below the FSP is accompanied by.
In other words once the moisture content of wood reaches 30 percent no more dimensional changes will occur as more water is added to the wood. In most types of woods the fibre saturation point is at 25 to 30 moisture content. The fiber saturation point is the critical condition reached in the process of seasoning at which by definition the wood contains just enough moisture to saturate the cell walls without the presence of any additional moisture in the cell cavities.
The aim is to introduce to biologists the concept of the fibre saturation point FSP and the related research of material scientists and engineers on the thermodynamics and chemistry of water in timber and wood. This paper investigated the FSP values of 15 tropical Brazilian wood species covering all strength classes of. In this short webcast we briefly explain the Fiber Saturation Point FSP of wood and discuss the importanc of FSP.
A new method for determining the fibre saturation point FSP of whole never-dried wood is described. Enthalpy of melting values from differential scanning calorimetry DSC experiments are used to calculate the proportion of non-freezing water. Actly the same conception as fiber-saturation point Expressed in the terms that pertain specifically to its cellular structure the saturation point of a wood fiber may be considered as the state in which the cavity of the fiber is entirely free from.
It applies to an individual cell or group of cells not to whole boards. Definition of fiber saturation point. The fibre saturation point FSP was estimated using an empirical relation where ρ w is the density of liquid water for derivation see eqn C5 in Roderick Berry 2001 that describes the general trend of decreasing FSP as D increases Skaar 1988 fig.
Two methods for calculating the FSP from the enthalpy data are described. They are more cost effective as predryers but are still not as cost competitive as air drying for this purpose. Plant-water relations and the fibre saturation point.

Fiber Saturation Point For Dried And Never Dried Pinus Radiata Pulps Download Scientific Diagram

Relationship Between Fibre Saturation Point And Density Of Tested Download Scientific Diagram

Estimation Of Fibre Saturation Point Slika 1 Odre Ivanje Procijenjene Download Scientific Diagram

Fibre Saturation Point An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Fibre Saturation Point An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Moisture Content Of Wood Youtube

Wood Structure And Properties Hardwood Softwood 1 Functions

Fibre Saturation Point An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Fibre Saturation Point An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Fibre Saturation Point An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

1 Free And Bound Water In Wood Download Scientific Diagram

Fiber Saturation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Fibre Saturation Point An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Fiber Saturation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Fiber Saturation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

What Is Fiber Saturation Point Fsp Of Wood Youtube
Inspecting And Testing Subfloors Moisture In Subfloors Moisture In Wood

Pdf Determination Of Fibre Saturation Point Of Selected Tropical Wood Species Using Different Methods

What Is Fiber Saturation Point Fsp Of Wood Youtube
0 Response to "fibre saturation point"
Post a Comment